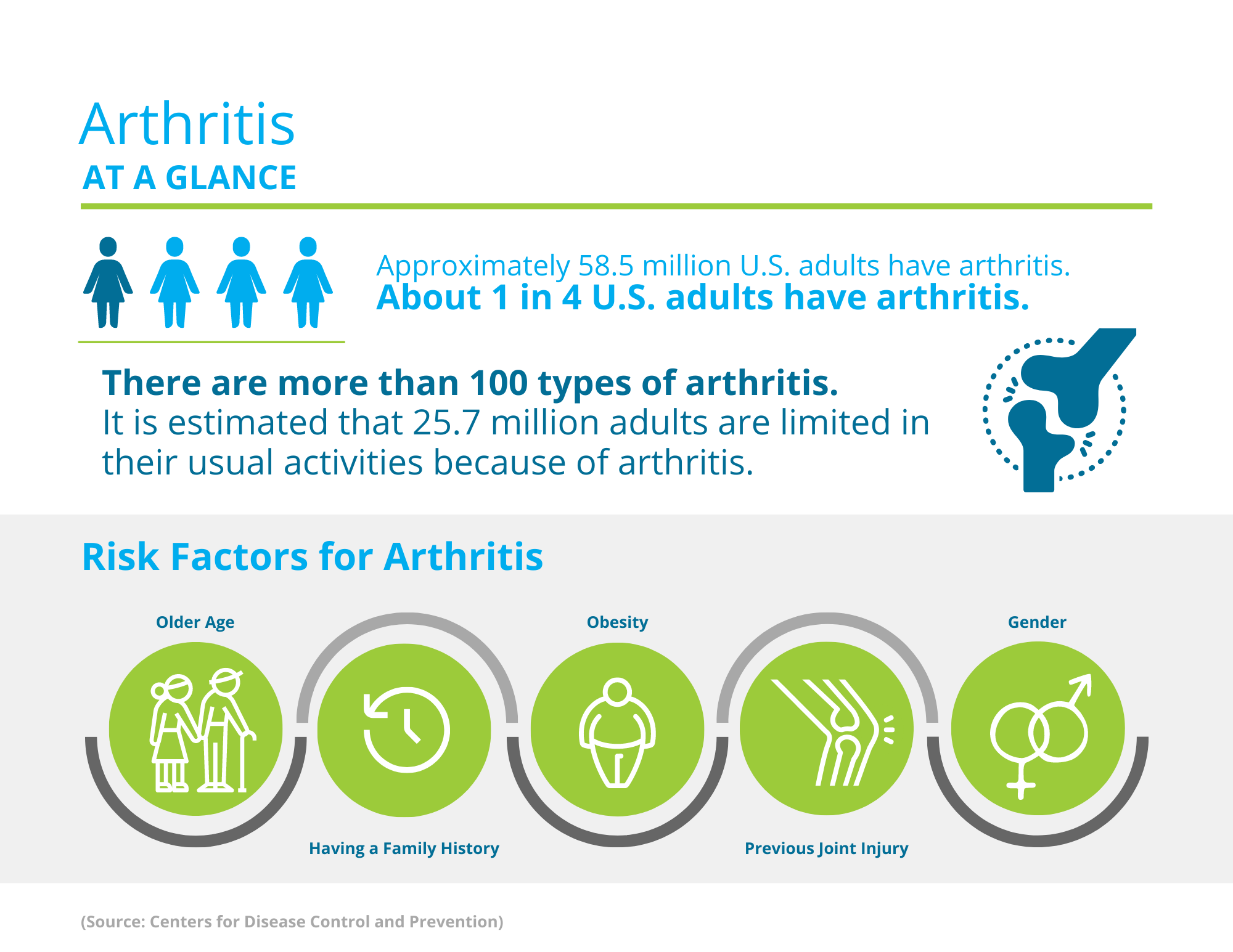
Arthritis is when joints, such as the knee, become swollen and tender. Arthritis affects many individuals, and worsens with age. The causes and treatments vary depending on the type of arthritis. There are two main forms of arthritis that will be discussed – Osteoarthritis and Rheumatoid arthritis.
For more information: https://www.cdc.gov/arthritis/index.htm
Osteoarthritis is known as one of the most common forms of arthritis. This form affects many individuals worldwide. Any joints in the body can be affected by osteoarthritis. However, the joints most commonly affected are the hips, knees, hands, and back. Symptoms can range from mild to the hindering of joint usage due to pain and stiffness. Some of the risk factors that lead to an increased chance of arthritis diagnosis are aging, obesity, gender, genetics, medical history, and previous injury or trauma. Diagnostic testing can be done by a physical exam, blood work, x-ray, or MRI. Osteoarthritis is not reversible, however there are some treatment options to help relieve symptoms. Treatment options are oral medication, over the counter medication, therapy, injections, surgery (such as joint replacement), and at home care.
For more information: https://www.cdc.gov/arthritis/basics/osteoarthritis.htm
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is an autoimmune disease (see autoimmune diseases for more information). This disease can affect the joints as well as other areas in the body. Rheumatoid arthritis affects the lining of your joints, which over time can cause joint deformity. The cause of RA is not specified down to one thing. However, there are risk factors that increase the chance of RA. Risk factors include previous virus or bacteria infections, family history, age, smoking, and obesity. Ra is diagnosed by physical exam, blood work, x-ray, or MRI. There is no cure for RA, however there are treatment options available to help slow progression and relieve symptoms. Treatment options include over the counter medication, prescribed medication, joint fusion, joint replacement, or additional surgery/ Speak with your doctor about your risk for RA.
For more information: https://www.cdc.gov/arthritis/types/rheumatoid-arthritis.html


