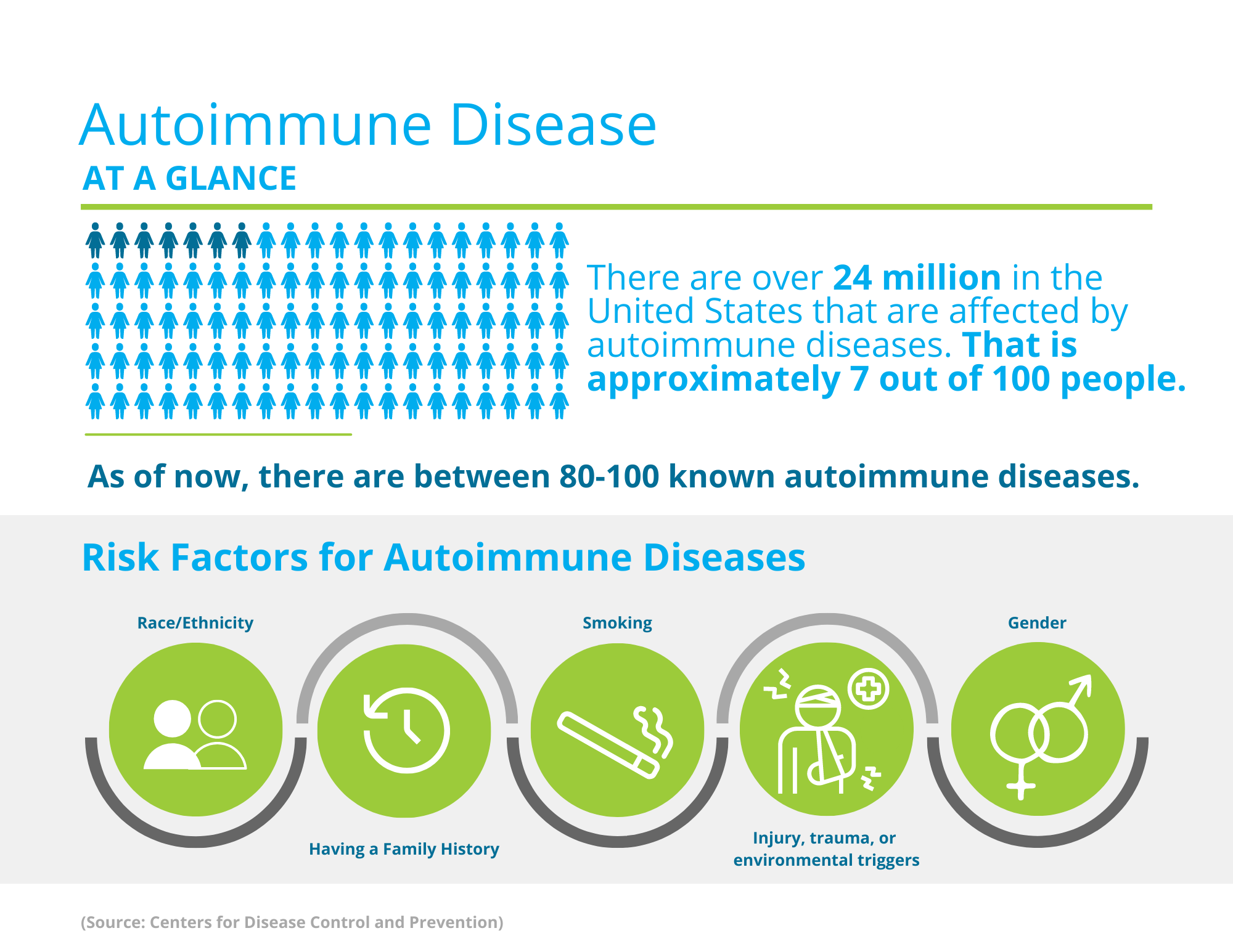
What are autoimmune diseases?
The immune system in the body has a job to protect the body by attacking foreign substances such as a bacterial infection. However, in a person with an autoimmune disorder the immune system attacks the body’s normal cells. Autoimmune diseases can affect several different areas of the body. Autoimmune diseases are more common than one may think. About 1 in 15 people in the United States have an autoimmune disorder. Autoimmune diseases are not contagious. There is no known cause for why the body’s immune system attacks itself. Family history is a well-known risk factor that increases the chance of developing an autoimmune disease. Past medical history, trauma or injury, gender, race, ethnicity, smoking, toxins, poor diet, and poor exercise can all also be risk factors for developing an autoimmune disease.
Examples of autoimmune diseases?
There are more than 80 autoimmune disorders. Listed are just a few common diseases, please visit the link for more diseases. Rheumatoid arthritis, Lupus, Inflammatory Bowel Disease, Multiple Sclerosis, Diabetes type 1, Psoriasis, and many more.
A more detailed list with links to learn more about specific autoimmune disorders: https://my.clevelandclinic.org/health/diseases/21624-autoimmune-diseases
Diagnosis & Treatment?
Autoimmune disease diagnosis will vary on disease type or concern. Some common diagnostic testing includes a physical exam with a complete history, blood work, x-ray, or MRI. A primary care doctor may be able to diagnose an autoimmune disease. However, they may send you to a specialist such as a rheumatologist.
Treatment for autoimmune disease also varies on disease, progression, and doctor recommendation. Different treatment options include over the counter medication, prescription medication, surgery, injections, sleeping medication, or rash cream. Your doctor will work with you to find the best treatment option for you.
For more information: https://www.niaid.nih.gov/diseases-conditions/autoimmune-diseases


