What is High Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is something that everyone has, and is found in everyone’s body. However, when cholesterol builds up this leads to High Cholesterol (Hyperlipidemia), and becomes a medical condition. Once cholesterol levels become high, then fatty deposits can develop within your blood vessels. The deposits can increase in size, causing less blood flow. In addition, the deposits can break off and form a blood clot that can lead to more serious conditions. There are two main types of cholesterol, and this depends on the proteins they attach to in your body:
Low-density lipoprotein (LDL) – this is referred to as the “bad” cholesterol. This is the type of cholesterol that builds up in the arteries.
High-density lipoprotein (HDL) – known as the “good” cholesterol. This type brings back extra cholesterol in your body and takes it to the liver.
Causes?
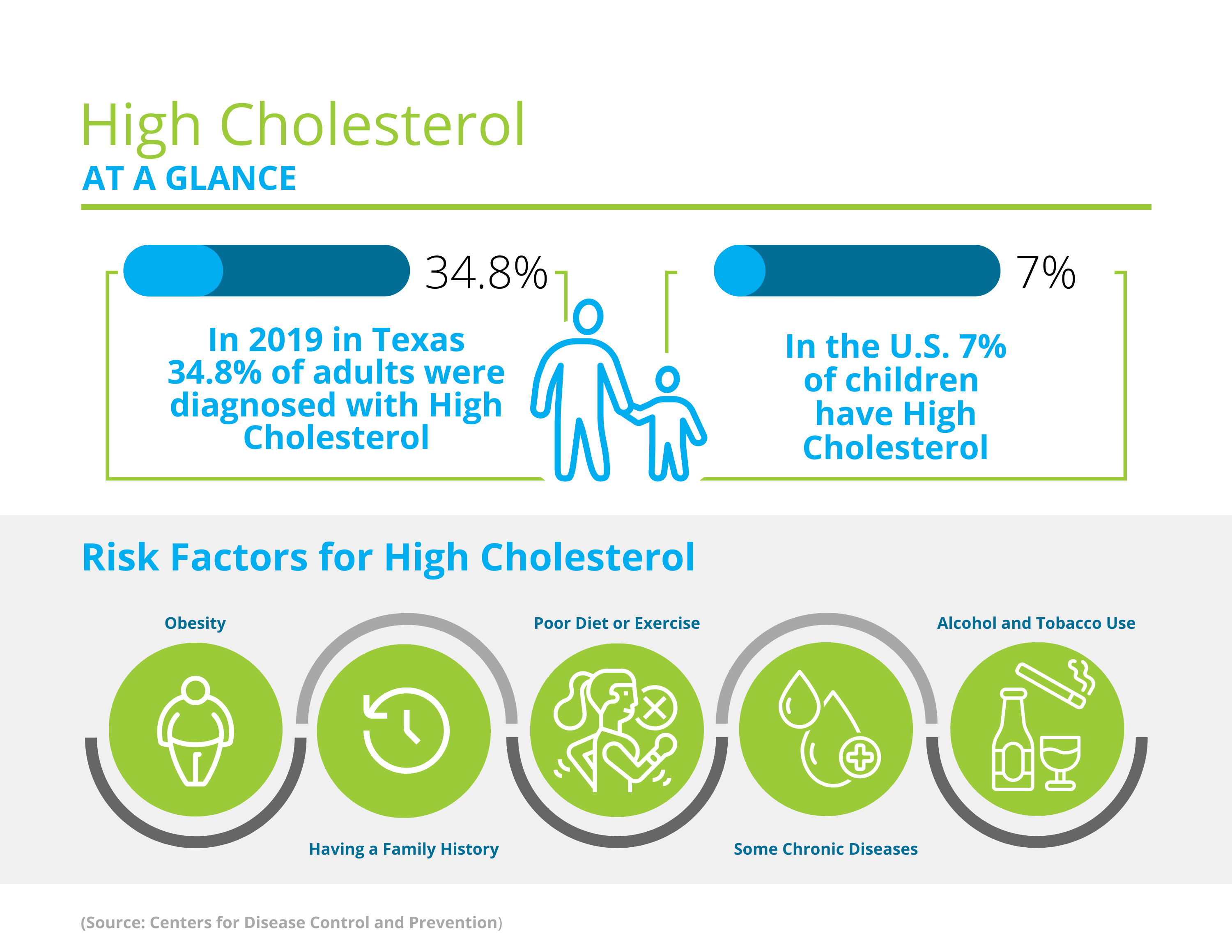
Cholesterol build-up to the point of high cholesterol diagnosis can be inherited, due to other medical conditions, or caused by lifestyle choices. Some of the lifestyle choices that may make a person more prone to high cholesterol are obesity, poor exercise, or poor diet with frequent foods such as sweets or processed foods. A few of the medical conditions that may make it harder for your body to get rid of the “bad” cholesterol are HIV/AIDS, diabetes, hypothyroidism, or chronic kidney disease. Certain medications, age, excessive alcohol use, and smoking can all also be risk factors for high cholesterol.
Diagnosis & Treatment?
The main form of diagnostic testing for high cholesterol is blood work. A doctor will order a lipid profile that will test the total cholesterol in the blood, the amount of LDL, the amount of HDL, and total triglycerides (type of fat) in the blood. They will then compare results, and determine diagnosis. Doctors may provide special instructions for blood tests, so make sure you follow what the doctor says to do (for example: a doctor may say not to eat prior to testing).
Your doctor will determine the best treatment for you, and if medications are needed. Some doctors may start with lifestyle changes such as increasing exercise and improving diet. Other doctors may go ahead and prescribe medication to help control cholesterol. Also, some doctors may combine both methods. Treatment plans will be determined by your doctor’s recommendation, and your cholesterol levels and medical history.
Prevention?
Prevention for high cholesterol includes managing risk factors for this chronic disease. Diet changes that may help lower the chance of high cholesterol diagnosis is consumption of more fruits and vegetables, presence of whole grains in diet, and animal fats in moderation. In addition to diet, an exercise routine may help reduce risk. Additional prevention techniques are to quit smoking, drinking alcohol in moderation, maintain a healthy weight, manage stress, and talk to your doctor about your risk of developing high cholesterol.
For more information: https://www.cdc.gov/cholesterol/index.htm


